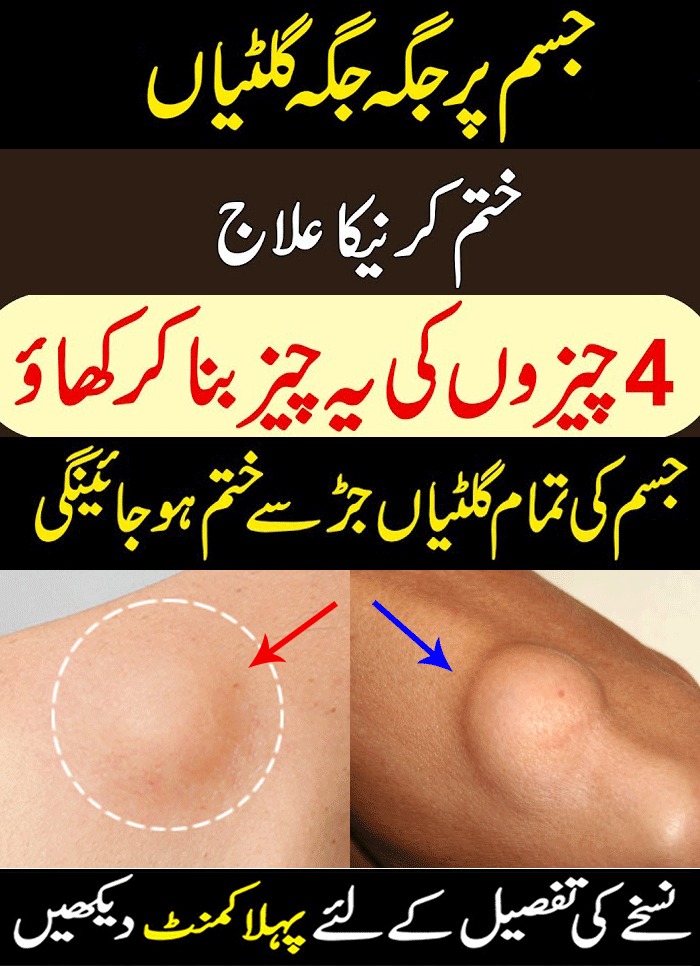
Lipomas are non-cancerous lumps caused by an overgrowth of fat cells. They can form anywhere on the body but are most common on the neck, shoulders, abdomen, and back. They are usually just under the skin, shaped like a dome, and soft to touch. They occur in about one in every 1,000 people in the US. and about one in 100 people in the UK.
Advertisement
Doctors are unsure of what causes lipomas, but believe it may be due to an inherited faulty gene or physical trauma. Most do not cause any pain unless they are deep in the body and press on nerves or organs. If a lipoma affects the bowels, it may cause constipation and nausea.
Lipoma Treatment by Dr Sharafat Ali Gilti Ka Ilaj
Early Signs and Symptoms of Cancer
How to Get Rid of Fatigue Naturally
Type-2-Diabetes-and-urination
Most lipomas do not need removing, but surgery may be necessary if the growth is large, causing symptoms or unsightly.
What are the symptoms of a lipoma?
Lipomas aren’t usually painful, but they can be uncomfortable if they press against a nerve or develop near a joint. Many people who have lipoma don’t notice any symptoms. Lipomas are usually:
Encapsulated: They don’t spread to the tissues surrounding them.
Painless: However, some lipomas cause pain and discomfort depending on their location, size, and if blood vessels are present.
Round or oval-shaped: The fatty lumps of rubbery tissue are usually symmetrical.
Moveable: They sit just beneath the skin’s surface and move when you touch them.
Smaller than 2 inches in diameter: In a few cases, lipomas can be larger than 6 inches wide.
Providers usually diagnose a lipoma during a physical examination. Your provider will touch the lipoma and ask if it’s painful or tender. You may need a biopsy to confirm that the lipoma isn’t cancer. During this procedure, your provider removes a sample of the lipoma and sends it to a lab for testing.
What is the treatment for lipomas?
Most lipomas don’t need treatment. If a lipoma is bothering you, your provider can remove it surgically. Lipoma removal procedures are safe and effective, and you can usually go home the same day.
As an alternative to lipoma surgery, your provider may recommend liposuction to remove the lipoma. Your provider uses a long, thin needle to remove fatty tissue from the growth.
What causes lipoma?
Healthcare providers aren’t sure what causes lipomas to grow. They are inherited (passed down through families). You’re more likely to develop a lipoma if someone in your family has one.
Some conditions cause multiple lipomas to form on the body. Lipoma-causing conditions include:
Dercum’s disease: This rare disorder causes painful lipomas to grow, most often on the arms, legs, and trunk. It’s also called adiposis dolorosa or Anders’ syndrome.
Gardner syndrome: A form of a disorder called familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Gardner syndrome causes lipomas and a range of health problems.
Hereditary multiple lipomatosis: Also called familial multiple lipomatosis, this disorder is inherited (passed down through families).
Madelung’s disease: This condition occurs most often in men who drink alcohol excessively. Also called multiple symmetric lipomatosis, Madelung’s disease causes lipomas to grow around the neck and shoulders